Unit – 3
[Notes Authored by Prof. Sayyed Muddassar N., IMS A’Nagar]
Decision Support Systems
Content
- Decision Support Systems
- Data Warehousing
- Data Mining
- Business Intelligence and Analytics
- Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS)
- Executive Information Systems/ Executive Support Systems (EIS/ESS)
- Geographical Information Systems (GIS)
- Knowledge Based Expert Systems/Expert Systems (KBES/ES)
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Importance of MIS in Management
Types of decision:-
- Strategical, Tactical & Operational
- Structured/Programmed – Routine, repetative
- Unstructured/Non Programmed – Non-routine, non-repetative
Relevance/Importance of MIS in Management
Evolution of DSS
- Initial concept – processing data, reports – General format – Distinction between data : information – Data analyzed in many ways/angles – MIS became individual oriented – Exception reporting – Need based exception reporting – Further decentralization of system – multiple databases – anybody handling system – Decision Support system
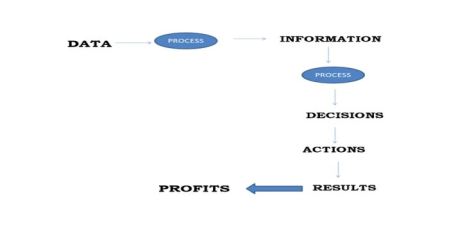
Decision Making Process
Definition – Decision Support System (DSS)
- A Decision Support System (DSS) is a computer-based information system that supports organizational decision making activities
- DSS help management to make decisions on Unstructured and Semi-Structured problems
- Does not give a decision itself
Characteristics of DSS
- Facilitation : Helps to make decision process easy
- Interactive : Two way, User – System
- Task-Oriented: Based on spefic tasks
- Ancillary : Act as secondary support mechanism to decision making
- Repeated Use: Reusable
- Identifiable: Easily identified
- Decision Impact: Impact on decision making
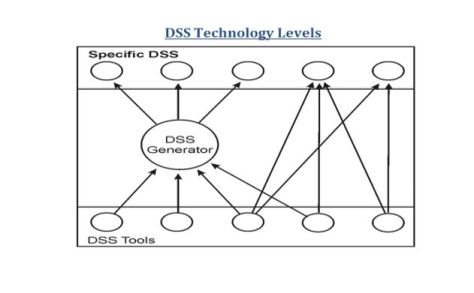
DSS Technology Levels
Sprague and Carlson (1982) identified three levels of DSS technology:
- Specific DSS : Systems that actually accomplish the work is SDSS
- DSS Generators : Integrated easy-to-use package with diverse capabilities ranging from modeling, report generation, graphical presentation
- DSS Tools : Lowest level/fundamental level and consists of software utilities of tools
Decision Support System Components

- Data Management :
- Storing and maintaining the information
- Model Management :
- It consists of both the DSS models and the Model Management System
- Interface Management :
- This component allows user – system interaction. It consists of the user interface management system
Data Warehousing
- A method to provide data to decision
- Data warehousing is the process of creating, populating, and then querying a data
- “A warehouse is a subject-oriented, integrated, time-variant and non-volatile collection of data in support of management’s decision making process“ – Bill Inmon
Characteristics of Data Warehousing
- Subject– Oriented: It is related to specific subject
- Integrated : All sub data are integrated into one warehouse
- Non- volatile : Changes made only manualy
- Time Variant : Data is in context with time
- Accessible : Easily accessible
- Process-Oriented: Data related to specific process
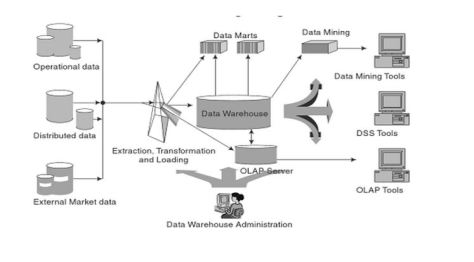
Components of Data Warehousing Architecture
Advantages of Datawarehousing
- Potential High Returns on Investment
- Competitive Advantage
- Increased Productivity of Corporate Decision-Makers
- More cost-Effective Decision-Making
- Better enterprise intelligence
- Delivers and Enhanced Business Intelligence
- Saves Time
- Enhances Data Quality and Consistency
- Provides Historical Intelligence
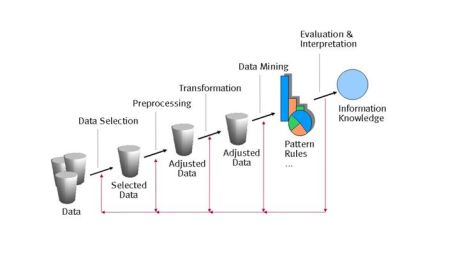
Data Mining
- Data mining/knowledge discovery, is the computer-assisted process of digging through and analyzing enormous sets of data and then extracting the meaning of the data
- “Data Mining, or Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD), is the extraction of implicit, previously unknown, and potentially useful information from data.
Data Mining Architecture
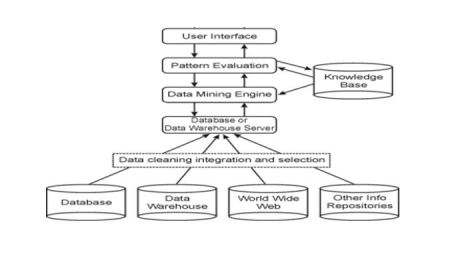
Components of Data Mining
- Database, Data Warehouse or Other Information Repository
- Database or Data Warehouse Server
- Knowledge Base
- Data Mining Engine
- Pattern Evaluation Module
- Graphical User Interface
Data Mining Process
Business Intelligence (BI)
- Business intelligence (BI) is a set of Technologies for gathering, storing, analyzing and providing access to information to help enterprise users make better business Decisions
- BI is used at all three levels
BI is useful in following areas:-
- Market research, analysis, segmentation
- Customer profiling, Loyalty
- PLC
- Distributor/sales analysis
- Reporting
- KM
- Supply Chain analysis
- Behavioral Analysis etc……
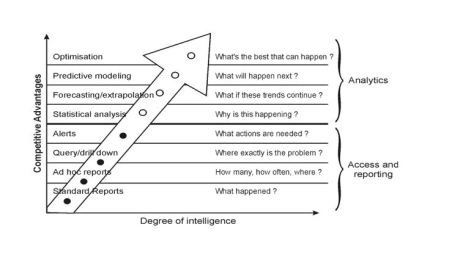
Business Analytics (BA)
- Organizations are data rich – information poor
- Extensive data use – statistical/quantitative analysis – fact based management – decision making – performance
- BA is the combination of skills, technologies, applications & processes used by organizations to gain insight into business based on data & statistics to drive business plan
Business Intelligence and analytics

GROUP DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM (GDSS)
- GDSS is an interactive computer based system that facilitates a number of decision-makers (working together in a group) in finding solutions to problems that are unstructured in nature.
Components of GDSS
- Hardware
- Software Tools
- People
- Procedures
Features of GDSS
- Support for Dispersed Group
- Technology-Assisted Meetings
- Better Decision Making
- Emphasis on Semi-structured and Unstructured Decisions
- Supports all Phases of the Decision Making
Executive Information System (EIS/ESS)
- EIS is a specialized Decision Support System with the help of this, executives get a great support in taking and performing the various types of the decisions
- Specialized form of DSS
- Executives work nature is special
- The emphasis of EIS is on graphical displays and easy-to-use user interfaces
Characteristics of EIS
- Display graphs and reports from the business processes of an organization
- Provides trends, analysis, exception reporting
- Easy to use: Both System design and interface design
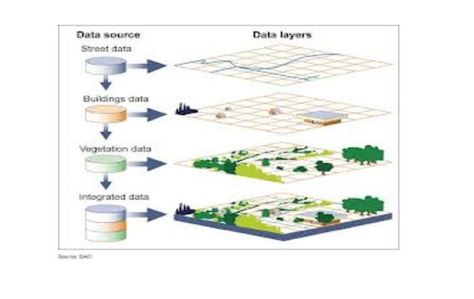
Geographical Information Systems (GIS)
- GIS is a computer system capable of assembling, storing, manipulating, and displaying geographically referenced information, i.e. data identified according to their locations
- A GIS is a system that provides spatial data entry, management, retrieval, analysis, and visualization functions
- For decision making
GIS Components

Applications of GIS
- Marketing/Advertising
- Archeology
- Cartography – Map making
- Site selection
- Election administration
- Distribution network
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- John McCarthy, who coined the term in 1955, defines it as “the science and engineering of making intelligent machines
- AI is a branch of computer science that is concerned with the automation of intelligence behavior
- Human intelligence – Use of sensory organs, creativity, imagination, learning from past, adaptive, language, emotions etc
- Machine Intelligence – Complex calculations, Information transfer, Repetitive work without error
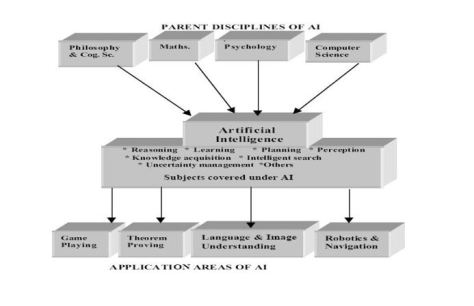
Objectives of Artificial Intelligence
- Understand Human
- Cost-Effective Automation
- Cost-Effective Intelligence Amplification
Knowledge Based Expert System/Expert System(KBES/ES)
- “An expert system is a computer program that represents and reasons with knowledge of some specialist subject with a view to solving problems or giving advice.”
- medicine, chemistry, finance etc.
Architecture of an Expert System
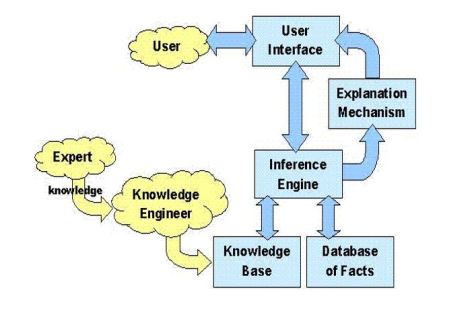
FEATURES OF ES
- Problem solving in the area of expertise
- Relying heavily on domain knowledge
- Explanation: Ability to explain results to user
- IF-THEN RULES
- If condition P, then conclusion C
- If situation S, then action A
- If conditions C1 and C2 hold, then condition C does not hold
Important Questions
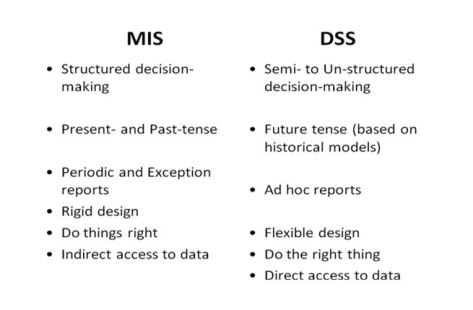
- Difference in MIS & DSS
- Data Warehouse
- Data Mining
- Explain concept of Data Warehousing. Discuss need of DW in modern business.
- Define DSS. Explain components of DSS.
- Explain GDSS/ES/EIS/GIS in detail.
Example Application Based Questions
- ‘A top level management always needs an exclusive information system for decision making’. Comment on statement in context of EIS/ESS.
- Compare different information systems for different managerial levels with explanation.
- Explain how expert system will help in improving performance of manufacturing firm.
- “Data Warehousing & Data Mining capacities can act as competitive advantage”. Do you agree? How?
- “Artificial Intelligence is the future”. Do you agree this statement? Explain.
[Notes Authored by Prof. Sayyed Muddassar N., IMS A’Nagar]
Quick Links: